
The OST-HER2 LM Vaccine is an immunotherapy approach targeting HER2-positive cancers such as osteosarcoma, breast, and esophageal cancer. It activates the body's immune system to fight cancer more effectively by training T cells to seek out and destroy cancer cells.
T cells attack cancer cells directly, creating holes and causing the contents to spill out, revealing new targets for the immune system to attack.
The OST-HER2 LM Vaccine shows promise in preventing or eliminating recurrences of osteosarcoma, particularly through translational research and trials involving canines diagnosed with the disease.
The OST-HER2 LM Immunotherapy shows promise in preventing or eliminating recurrences of human osteosarcoma.
The OST-HER2 LM Immunotherapy shows promise in treating canine osteosarcoma.
The intravenous OST-HER2 vector is rapidly cleared by the immune system’s Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs), which then activate potent HER2-specific T cells.
The destruction of cancer cells exposes additional targets, perpetuating a cycle of immune activation and sustained therapeutic effects.
Activated T cells proliferate, travel through the bloodstream, and target cancer micro-metastases, where they infiltrate the cancer cells. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) that protect tumors are reduced.
The OST-HER2 LM Vaccine shows promise in preventing or eliminating recurrences of osteosarcoma, particularly through translational research and trials involving canines diagnosed with the disease.

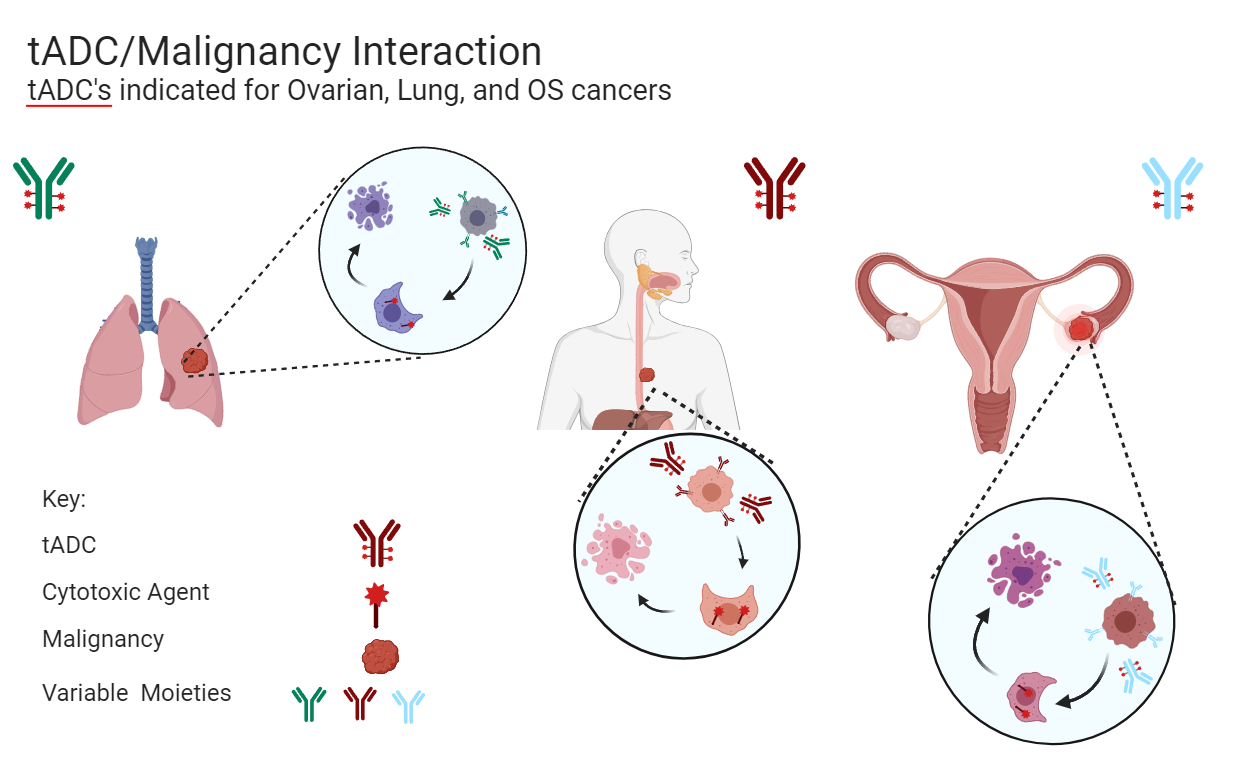
tADCs (targeted antibody-drug conjugates) selectively bind to specific receptors on cancer cells. Once bound, the tADC is internalized into the cancer cell through endocytosis.
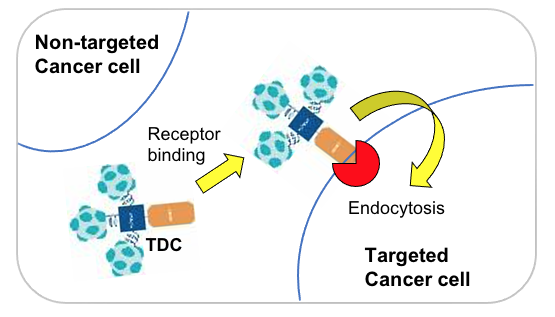
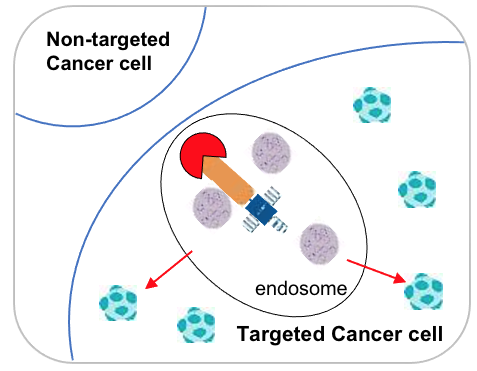
After internalization, the tADC complex is transported to the cell's endosome or lysosome. In this acidic environment, the SiLinker is cleaved, releasing the active CAPs (cell-penetrating agents), which are then prepared to cross cell membranes.

Once released, CAPs permeate out of the endosome and disperse within the targeted cancer cell. Physiological pH within the cancer cell retains CAPs inside, amplifying the cell-killing effect.
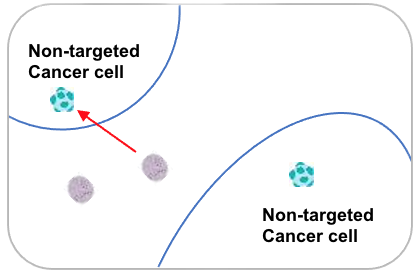
The acidic necrotic core of large tumors allows CAPs to penetrate nearby cancer cells as well, including non-targeted cancer cells. This "bystander effect" extends anti-tumor activity beyond the initially targeted cells, while normal pH outside the tumor prevents CAPs from entering healthy tissue.
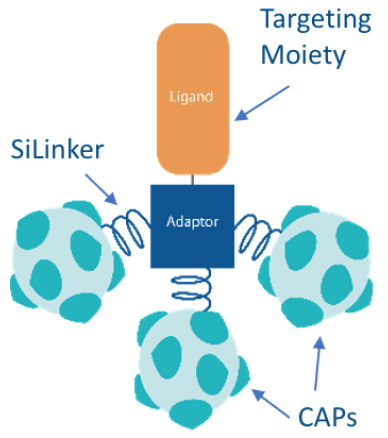
OST-tADCs (Tunable Drug Conjugates) are designed to improve the efficacy and safety of cancer treatments. These advanced therapies use smaller targeting moieties, or ligands, to achieve better tumor penetration, enhancing the ability to attack cancer cells directly.
Meet our Osteo-AngelsSmall ligands facilitate rapid clearance of tADCs from the body, reducing systemic toxicity.
SiLinkers are stable under normal physiological conditions, ensuring the payload is only released in targeted areas.
CAPs do not readily enter normal cells, minimizing the risk to healthy tissues.
OST-tADCs are chemically assembled, allowing for precise control over the number of toxin payloads attached to each conjugate. This method ensures the final product is highly purified and ready for targeted therapeutic use.